大形コンベヤチェーン
製品情報 大形コンベヤチェーン
大形コンベヤチェーンとは、水平、垂直、傾斜など自由に組み合わせていずれの方向にも輸送が可能、温度に対しては200度程度まで特殊材質を使う必要がなく、高温になれば耐熱鋼を使用、また水や薬品に対しても耐食性・耐薬品性を有する仕様がある、運用範囲が広いチェーンです。
微粉炭、セメントなどの粉末から小麦大豆などの粒状のもの、鉱石、岩石などの塊状のもの、1個数トンに及ぶ製品まで、ほとんどあらゆる運搬物を運ぶことができ、運搬物に対する制限はほとんどありません。
大形コンベヤチェーン関連情報
-
選定
-
資料
-
運用
構造

※大形コンベヤチェーンの全長公差は±0.25%です。
■すきまばめ
軸と穴を組み合わせたときに、常にスキマができるはめあい。
穴の公差域が完全に軸(ピン、またはブシュ)の公差軸の上側にあるはめあい。
■しまりばめ
軸と穴を組合せたときに、常に締めしろができるはめあい。
穴の公差域が完全に軸(ピン、またはブシュ)の公差域の下側にあるはめあい。
| 1.ピン(CP) | 2.ブシュ(B) | |
|---|---|---|
| ピンは外リンクと内リンクを連結することが最も重要な役目です。プレートと同様、進行方向にチェーン張力を受け、直角方向に運搬物の反力を受けます。さらにピンの外周はチェーンが屈曲するときに、ブシュの内周と摺動して摩耗します。ピンは重要な強度部材であると同時に耐摩耗性が要求されます。 | ブシュはスプロケットにチェーンが噛合う時、チェーン張力を受ける強度部材ですが、主要な働きは軸受部材です。ブシュの外周は、ローラが回転するときにはローラの内周との摺動により摩耗し、ブシュの内周は、チェーンが屈曲するときピンの外周と摺動して摩耗します。ブシュの内周の摩耗は直接ピッチ伸びとしてあらわれます。 | |
| 3.ローラ(R-R, F-R, S-R, M-R, N-R) | 4.プレート(PLP-A, PLP-B, BLP) | |
| ブシュと「すきまばめ」になっています。スプロケットに噛合う時はコロの働きをして、衝撃および歯面の摩耗を緩和します。また走行するときは転がって走行抵抗を少なくします。 | プレートは主としてチェーンの進行方向に引張り荷重を受け、直角方向に運搬物を支えるための反力を受けます。チェーンが屈曲するときは外プレートと内プレートが摺動し、スプロケットに噛合う時は歯の側面と摺動します。一般に外プレートには丸穴と欠穴があります。 | |
| 5.Tピン(T-PIN) | 6.アタッチメント | |
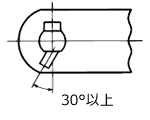 |
外プレートにピンを圧入後、Tピンを挿入し、曲げてピンの抜け止めとします。30°以上曲がるか、Tピンの端がプレートの幅以内に納まるまで曲げておきます。 | 取付物を固定する部分です。 アタッチメントの種類については下記の「アタッチメントの種類」をご覧ください。 |
■チェーンの基本3寸法
ピッチ、ローラ径、内リンク内幅をローラチェーンの基本3寸法といいます。この寸法が同一のときは、ローラチェーンとスプロケットは寸法的には互換性があります。
アタッチメントとは、搬送ジグをチェーンに取付けるための部品です。ご要望のリンク間隔で組込みが可能です。
標準アタッチメント
経済的で汎用性のあるアタッチメントです。
Aアタッチメント
片側に羽根のついた形式です。
ボルト穴の数でA1, A2, A3と呼びます。
A1アタッチメント

A2アタッチメント

A3アタッチメント

Kアタッチメント
両側に羽根のついた形式です。
ボルト穴の数でK1, K2, K3と呼びます。
K1アタッチメント

K2アタッチメント

K3アタッチメント

GAアタッチメント
片側のプレートにボルト穴のある形式です。
ボルト穴の数でGA2, GA4と呼びます。
GA2アタッチメント

GA4アタッチメント

専用アタッチメント
各用途専用のアタッチメントです。
ディープリンク

トップローラ

サイドローラ

フロー用

特殊アタッチメント (プラスαコンベヤチェーン)
特殊アタッチメントのバリエーションです。
SAアタッチメント付
片側に垂直羽根のついた形式
SKアタッチメント付

両側に垂直羽根のついた形式
CA2アタッチメント付

ネットの取付
隙間なしのスラット取付用
AA3アタッチメント付

アタッチメントを挟み込む強力形
AR2アタッチメント付

Aアタッチメントの曲げ剛性を向上
(補強リブ付)
MG2アタッチメント付
1種類の取付ジグで使用できる
AS2アタッチメント付
スクレーパやフライト取付
AF2アタッチメント付
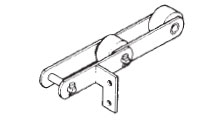
深いスクレーパやフライト取付
WSA0アタッチメント付
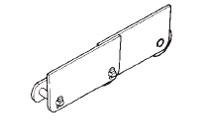
輸送物のこぼれ防止
延長ピン付
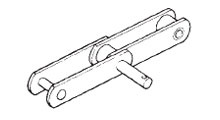
ピンの端部に取付可能
(形式 : EN)
ステーピン付

繋ぎピンに直載せ
ネットなどの取付
(形式 : TN)
トッププレート付

輸送物にキズをつけない
(形式 : TP)
トロリーローラ付
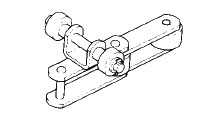
水平の長距離用
(形式 : TRO)
アウトボードローラ付
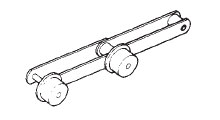
大荷重の支持
(形式 : RO)
ガイドシュー付

横振れ防止
(形式 : GS)
ガイドローラ付

水平使用
(形式 : GR)
固定ドッグ付
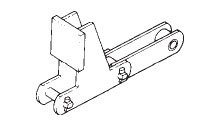
押して搬送
(形式 : KD)
ドッグローラ付

丸物を押して搬送
(形式 : RD)
チルチングドッグ付

コンベヤ上でのストレージ
(形式 : CD)
ローラチルチングドッグ付
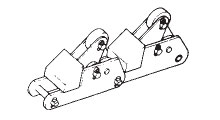
丸物のストレージ
(形式 : RCD)
ダッキングドッグ付

定位置に搬送物を残す
(形式 : DD)
ローラの種類
大形コンベヤチェーンには、用途に応じて3つの基本的なローラ形式があります。
| 大形コンベヤチェーン 基本ローラ形式 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rローラ | Fローラ | S,M,Nローラ |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
スプロケットの噛み合い時に衝撃や摩耗を緩和する働きがあります。
|
大形コンベヤチェーンの円滑な運転のため、ローラ形式による運び側・戻り側のガイド方法例を次に示します。
ガイド方法例
| Rローラ(Sローラ)形チェーン | Fローラ形チェーン | サイドローラ付チェーン | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 運び側 |  |
 |
 |
| 戻り側 | 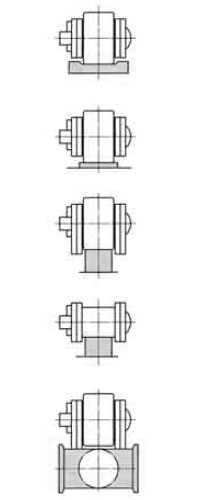 |
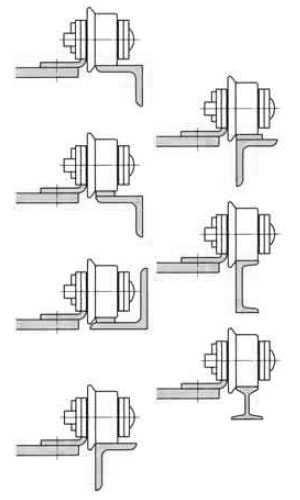 |
 |
安全上のご注意
組立てられたチェーンへの付加部品の溶接は、プレートの歪みによるチェーンの曲がりや捩れを生じ、また、熱影響による部品の硬度低下や脆性破壊を生じることがありますので、絶対に行わないでください。
大形コンベヤチェーン製品一覧
特殊大形コンベヤチェーン(バイオマス・発電所)
バイオマス発電設備におけるウッドチップ搬送用のドラグチェーンです。
下記以外にもバイオマス発電施設での過酷な用途に対応する各種コンベヤチェーンをご用意していますので、セレクションガイドからご参照ください。
ドラグチェーン WD形
形番 WD□□□~
チェーンで搬送物を直に押し出す用途に特化した専用チェーンです。
- ・プレートとブシュを溶接し、一体にしたスチール製チェーンです。
- ・ブシュ前面は搬送物を押せるように平らになっており、ブシュ背面はスプロケットと噛み合うように
丸くなっています。 - ・Cピン(連結ピン)の両端がTピン止めのため、シンプルな構造。
- ・引っ張り強さを向上した強力仕様や、腐食対策仕様も製作可能です。
- ・独自のアタッチメントとソリューションを提供(特形対応品)。
サイズ
WD480(WD112, 120), WD110
アタッチメント種類
スクレーパ:SCR
ガイドシュー:GS
※当社までご相談ください








