トラブルシューティング 小形コンベヤチェーン
チェーンおよびスプロケットは、著しい損傷や破壊があった場合は、以下の手当を行って新品に交換してください。
全般
| 1 | チェーンがスプロケットに乗り上げる |
|---|---|
| 2 | 異常な騒音がする |
| 3 | チェーンがスプロケットに巻込む(噛離れが悪い) |
| 4 | チェーンのプレートの内側とスプロケット歯側面の摩耗 |
| 5 | チェーンのプレート側面やピン頭部の摩耗 |
| 6 | チェーンの屈曲が悪い |
| 7 | プレート内幅の広がり |
プレート関係
| 8 | プレートの急進破壊 |
|---|---|
| 9 | プレートにクラックが発生(疲労) (引張方向に直角方向) |
| 10 | プレート穴の変形 |
| 11 | 応力腐食割れ(プレートに弓状のクラック) |
ピン関係
| 12 | ピンが破断する |
|---|---|
| 13 | ピンの回転または飛び出し |
ブシュ・ローラ関係
| 14 | ローラ・ブシュが割れる(脱落) |
|---|---|
| 15 | ローラが回転しない、ローラの片ベリ |
| 16 | ローラが開口する |
| 17 | ローラがつづみ形になる |

全般
| 1 |
 [クリックで拡大] |
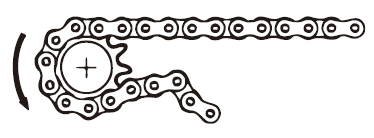
チェーンがスプロケットに乗り上げる |
|---|
| 原因1 | チェーンとスプロケットが不適合 | 手当法 | チェーンまたはスプロケットを正しいサイズに取替える。 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原因2 | 著しい過負荷 | 手当法 | 負荷を減少させる(被動機に給油なども)。またはチェーンの列数を増やすか、サイズを大きくする。 |
| 原因3 | チェーンの摩耗伸びまたはスプロケットの歯の摩耗 | 手当法 | 新品と取替える。 |
| 原因4 | 巻付角の不足 | 手当法 | 120°以上または3歯以上の巻付角とする。 |
| 原因5 | バックテンション不足 | 手当法 | カテナリ、テークアップの設置および調整。 |
| 原因6 | チェーンとスプロケットの心間距離 | 手当法 | 点検後、修正する。 |
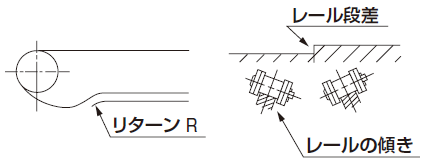
| 2 | 異常な騒音がする |
|---|
| 原因1 | スプロケットや軸の据付不良 | 手当法 | 点検・修正をする。 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原因2 | チェーンケーシングや軸受の緩み | 手当法 | 全てのボルト・ナットを締め直す。 |
| 原因3 | チェーンのたるみ量の過大・過小 | 手当法 | 最適のたるみになるように軸間距離を調整する。 |
| 原因4 | チェーンまたはスプロケットの著しい摩耗 | 手当法 | 一連のチェーン・スプロケットを新品に取替える。 |
| 原因5 | 無給油または給油不適当 | 手当法 | 使用条件に合った給油をする。 |
| 原因6 | チェーンまたは運行部とケーシングとの干渉 | 手当法 | 点検後、修正する。 |
| 原因7 |
ガードレールの設定不良 |
手当法 | 点検後、修正する。 |
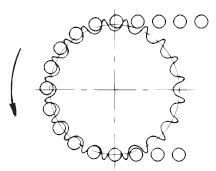
| 3 |
 [クリックで拡大] |
チェーンがスプロケットに巻込む(噛離れが悪い) |
|---|
| 原因1 |
チェーンのたるみ量が過大 |
手当法 | チェーン長さまたは軸間距離を調整する。 テンショナを付ける。 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原因2 | チェーンの摩耗伸び、またはスプロケットの摩耗 | 手当法 | いずれも新品と交換する。 |
| 原因3 | チェーンとスプロケットの不適合 | 手当法 | 新品と交換する。 |
| 原因4 | 発錆による屈曲不良 不適当な給油、悪い雰囲気 |
手当法 | チェーンを取替えた後で、給油やケーシングによって雰囲気からチェーンを保護する。 |
| 4 | チェーンのプレートの内側とスプロケット歯側面の摩耗 |
|---|
| 原因1 | 据付不良 | 手当法 | スプロケット、軸などの据付修正をする。 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原因2 |
チェーンが横方向に押される |
手当法 | 押される原因の除去、ガイドローラ付チェーンに変更する。 |
| 5 | チェーンのプレート側面やピン頭部の摩耗 |
|---|
| 原因1 |
ガイドなどの据付不良 |
手当法 | ガイドの状態をチェックし、ガイドとチェーンの隙間を広くする。 |
|---|
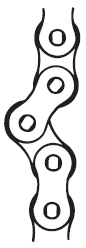
| 6 |
 [クリックで拡大] |
チェーンの屈曲が悪い |
|---|
| 原因1 | 据付不良によるローラチェーンの変形 | 手当法 | 据付状態の点検・修正をする。 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原因2 | 不適切な給油(例えばグリース)による摩耗粉、ゴミなどの固着 | 手当法 | チェーンを外し、洗浄・適切な給油をする。 |
| 原因3 | 過負荷、ピンの曲り、ブシュ割れ | 手当法 | 負荷を減少させる、またはチェーンサイズや列数を増やす。 |
| 原因4 | 腐食・錆 | 手当法 | ケーシングを付けてチェーンを保護する。 |
| 原因5 | 給油不足 | 手当法 | 給油を十分に行う。 |
| 原因6 | 異物・輸送物がクリアランスにつまる | 手当法 | ケーシングの取付けなどによりチェーンを保護する。 |
| 原因7 | 高温での使用 | 手当法 | 適正なクリアランスとする。(当社までご相談ください) |
| 7 | プレート内幅の広がり |
|---|
| 原因1 |
据付不良による偏荷重または著しい過負荷 |
手当法 | 新品に取替えると共に据付けの修正をする。 |
|---|
プレート関係
| 原因1 | 過大な衝撃荷重 | 手当法 | 起動・停止をスムーズにするなどによって衝撃荷重を小さくする。(緩衝装置を付けるなど) チェーンのサイズを大きくする、または列数を多くする。 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原因2 | チェーンの振動 | 手当法 | 振動を防止する装置を付ける。(テンショナ、アイドラなど) |
| 原因3 | 腐食 | 手当法 | 新品に取替える。ケーシングを付けてチェーンを保護する。また定期的にチェーンを洗浄し給油する。 |
| 9 | プレートにクラックが発生(疲労) (引張方向に直角方向) |
|---|
| 原因1 | 最大許容荷重よりも大きな負荷が作用 | 手当法 | 過負荷・過大繰返し荷重を除く、またはチェーンのサイズを大きくするか、列数を多くする。 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原因2 | アタッチメントに繰返し荷重が作用 | 手当法 | 過負荷がかからないようにする。またはチェーンのサイズアップを行い、アタッチメントの許容荷重を大きくする。 |
| 10 |
 [クリックで拡大] |
プレート穴の変形 |
|---|
| 原因1 | 過負荷 | 手当法 | 新品に取替える。過負荷の要因を除く。 |
|---|
| 11 |
 [クリックで拡大] |
応力腐食割れ(プレートに弓状のクラック) |
|---|
| 原因1 | 酸・アルカリ性雰囲気での使用 (繰返し荷重の影響ではない。) |
手当法 | 新品に取替える。ケーシングなどによって雰囲気からチェーンを保護する。 応力腐食割れに抵抗性の高い仕様の検討。 |
|---|
ピン関係
| 原因1 | 大きな衝撃荷重 | 手当法 | 衝撃を弱め、起動・停止をスムーズにする。 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原因2 | ピンの疲労限を越える繰返し荷重 | 手当法 | 過大繰返し荷重を除く、またはチェーンのサイズを大きくするか、列数を多くする。 |
| 原因3 | 腐食 | 手当法 | ケーシングを付ける。定期的にチェーンを洗浄し給油する。 |
| 13 |
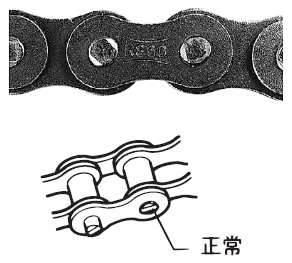 [クリックで拡大] |
ピンの回転または飛び出し |
|---|
| 原因1 | 過負荷または給油不足 | 手当法 | 新品に取替える。過負荷または給油の改善をする。 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原因2 | 高負荷で給油不良の場合に、ピンとブシュに異常な摩擦力が発生し、瞬時にピンが廻ることがある。この状態で運転すると、ピン抜けによってチェーンが破壊する。 | 手当法 | 直ちに新品に取替える。このときピンを溶接したり、古いピンの再使用はしないでください。(古いチェーンは誤って再使用しないように破棄してください)また、ピン頭部やプレート側面が摩耗しているときは、据付状態を点検してください。 |
ブシュ・ローラ関係
| 14 | ローラ・ブシュが割れる(脱落) |
|---|
| 原因1 | 不適切な給油 | 手当法 | 使用条件に適切な給油をする。新品に取替える。 |
|---|
| 15 | ローラが回転しない、ローラの片ベリ |
|---|
| 原因1 | RS25、RS35 | 手当法 | ブシュドチェーンでローラはありません。 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原因2 | 内プレートが内側に寄っている、またはブシュ割れ | 手当法 | 新品に取替える。据付の再点検、負荷のチェック |
| 原因3 | 輸送物・異物がブシュとローラ間に入る。 | 手当法 | 定期的な排除。ケーシングを取付けてチェーンを保護する。 |
| 原因4 | ローラ負荷が過大 | 手当法 | 荷重を軽減する。またはチェーンのサイズアップをする。 |
| 原因5 | 輸送物・異物がフレームに堆積 | 手当法 | 定期的に排除、仕切りを付けてチェーンを保護する。 |
| 原因6 | ブシュ・ローラの錆付き | 手当法 | 適正な仕様(材質)の再選定 |
| 原因7 | 内プレートが内側に寄る | 手当法 | 取替え、据付再点検、荷重の再点検 |
| 16 | ローラが開口する |
|---|
| 原因1 |
過負荷 |
手当法 | 負荷を減少させる。適切な給油をする。 |
|---|
| 17 | ローラがつづみ形になる |
|---|
| 原因1 | 過負荷または、給油不足 | 手当法 | 新品に取替える。過負荷または給油の改善をする。 |
|---|