技術資料 大形コンベヤチェーン 選定
2. コンベヤ形式の決定
| コンベヤ基本形式 | 搬送物 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| かずもの | チェーン形式 | ばらもの | チェーン形式 | |
| 搬送物を載荷する形式 | ・スラットコンベヤ
|
RF- [BR/BF] RF-(NB) RF RF-[DBR/DBF] |
・エプロン/パンコンベヤ
|
RF RF-(KG/KA) |
| ・プッシャコンベヤ・トウコンベヤ ジェットコースタ 
|
RF RF-(NB) NF RF-<SR> |
|||
・フリーフローコンベヤ
|
RF-[VR] RF-<SR> RF-<TR> |
|||
・プレーンチェーンコンベヤ
|
RF NF RF-(DL) |
|||
| 搬送物を懸垂する形式 | ・トロリコンベヤ | RF RF-<TRO> |
・バケットエレベータ | RF B |
・トレーエレベータ
|
RF NF |
・フライアッシュ用バケットエレベータ
|
RF-(FB) | |
・立体駐車機
|
RF 専用チェーン |
・バケット式連続アンローダ | 特殊チェーン | |
| 搬送物を押すまたは摩擦で動かす形式 | ・プッシャコンベヤ
|
RF NF RF-(NB) |
・スクレーパ/フライトコンベヤ
|
RF RF-(AM/AP) RF-(FG/FP) |
・水平循環コンベヤ
|
RF RF-(NB) RF-<GR> |
・フローコンベヤ
|
RF NFX |
|
| ・ドラグチェーンコンベヤ | WD | |||
注)
- 1. 搬送物の摩耗、腐食特性については各種溶媒に対する耐食性をご参照ください。
- 2. ()内は仕様記号、[]はローラ形式、<>は専用アタッチメント形式を示します。
3. チェーン形式の決定
チェーン形式の決定には、搬送物の性質を把握した上で搬送方法を決め、そのために最も経済的なチェーンコンベヤ形式を採用します。
コンベヤチェーンの使用方法は、上表の基本3形式とその他形式があります。用途に応じて前ページを参照のうえ、チェーン形式を決定してください。
| チェーン形式決定の留意点 |
|---|
|
4. ローラ形式の決定
大形コンベヤチェーンの構造の項の「ローラの形式」をご覧ください。
5. コンベヤチェーンの基本レイアウト
5.1 水平搬送の場合
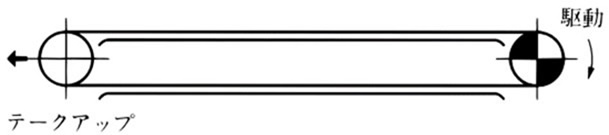
戻り側(図の下方)の一部または全部をカテナリとしたものは、チェーンの熱などによる伸縮を吸収できます。比較的低速の場合に使用可能で垂れ量は通常、スパンの1割程度が適当です。逆転のあるコンベヤに使用するのは困難です。
1) 駆動スプロケットの外れ側にカテナリをつくる方法
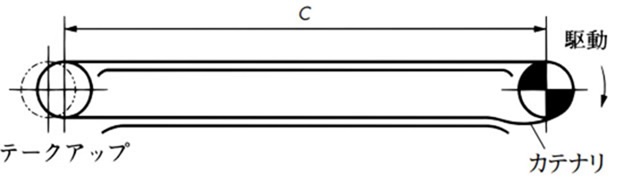
利点
- 1) カテナリ張力が駆動スプロケットの噛み合いを円滑にする。
- 2) チェーンに給油するときは、カテナリ部で行うと効果があります。
2) 戻り側を支持しない方法
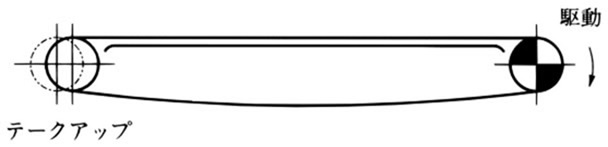
機長が短く、低速のときに使用できます。
戻り側のチェーン質量による張力が振動の原因になり、スムーズな搬送ができないこともあります。
3) 戻り側をガイドまたはローラで受ける方法
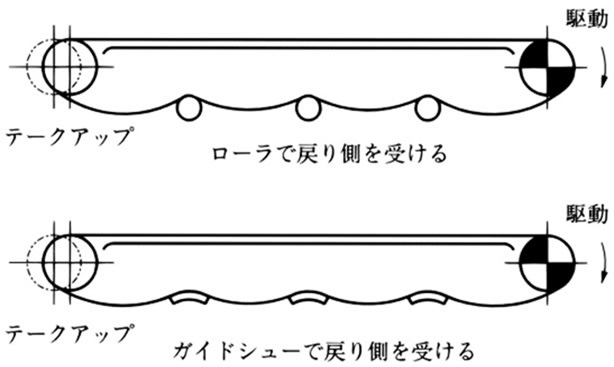
チェーンがガイド、ローラと接し屈曲するので摩耗を早めたり、きずを生じやすくなることがあります。
またチェーンの振動が悪影響をおよぼすことがあり、機長が長い場合は分割してカテナリで受けることがあります。
4) 戻り側をすべてガイドで受ける方法
戻り側をすべてレールで支え、従動側のスプロケットにテークアップを装着し、チェーンのたるみを吸収する方法です。逆転のある場合にも採用できます。
ただし、カテナリが駆動スプロケットを出たところにありませんので、定期的にチェーンの伸びをテークアップで調整する必要があります。
注)テークアップの張過ぎは、チェーンの摩耗を早める原因となりますのでご注意ください。
5) 戻り側が上方になる例
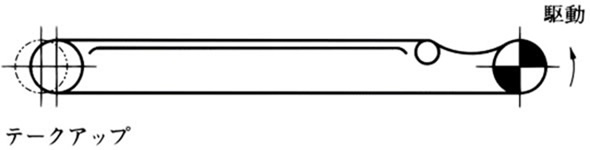
5.2 垂直搬送の場合
載荷のまま停止することがある場合は、逆転防止のため、駆動部にブレーキや、「つばきバックストップカムクラッチ」を設置する必要があります。
注)テークアップの張過ぎは、チェーンの摩耗を早める原因となりますので注意してください。
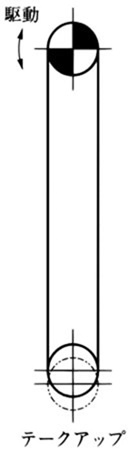
5.3 傾斜搬送の場合
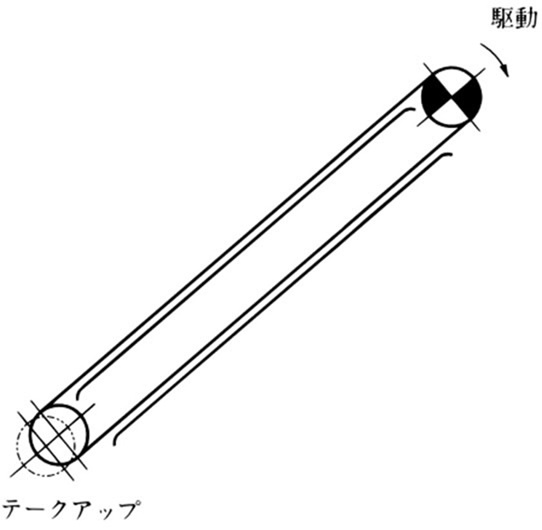
5.4 軸が垂直の場合
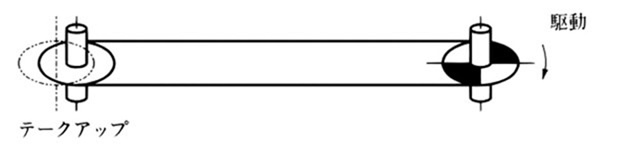
水平循環など軸が垂直の場合は、チェーンにガイドローラなどを取付けて、チェーンの運行をスムーズにします。
| コンベヤチェーン使用上の留意点 |
|---|
|
6. ばらもの搬送用チェーン仕様の決定
代表的なばらもの搬送物に使用されるチェーンコンベヤ形式、およびチェーン仕様を参考に掲げ、推奨チェーン仕様を示します。
搬送物によっては、同一名称でも状況・性質が表1と異なるものもありますので、従来の実績も考慮に入れ、十分にご検討のうえコンベヤ形式、チェーン仕様を決定してください。
表1. 搬送物とチェーン仕様
- 1. 搬送物の摩耗性については、大→中→小の順に摩耗性が小さくなることを示します。
- 2. 腐食性については、強酸性・酸性・中性・アルカリ性・強アルカリ性で示します。
- 3. 美麗仕様を使用するときは、美麗仕様をご参照ください。
| 搬送物 | 使用可能チェーンコンベヤ形式 | 推奨チェーン 仕様記号 |
備考 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 名称 | 摩耗性 | 腐食性 | スクレーパ コンベヤ |
フロー コンベヤ |
エプロン コンベヤ |
バケット エレベータ |
||
| 米 | 小 | 中性 | ○ | ○ | ○ | DT | ||
| 大麦 | 小 | 中性 | ○ | ○ | ○ | 〃 | ||
| 小麦 | 小 | 中性 | ○ | ○ | ○ | 〃 | ||
| 大豆 | 小 | 中性 | ○ | ○ | ○ | 〃 | ||
| トウモロコシ | 小 | 中性 | ○ | ○ | ○ | 〃 | ||
| 小麦粉 | 小 | 中性 | ○ | ○ | ○ | 〃 | ||
| でん粉 | 小 | 中性 | ○ | △ | △ | 〃 | ||
| ケーン(さとうきび) | 小 | 中性 | ○ | ○ | DTA | |||
| バガス | 小 | 中性 | ○ | DTA | ||||
| 精製糖 | 小 | 中性 | ○ | ○ | ○ | SS | 注)3参照 | |
| 岩塩 | 小 | 中性 | ○ | △ | △ | DT | ||
| 混合飼料 | 小 | 酸性 | ○ | △ | △ | 〃 | ||
| ソーダ灰 | 中 | 強アルカリ性 | ○ | △ | △ | 〃 | ||
| カーバイド | 中 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 〃 | ||
| 芒硝 | 中 | 酸性 | △ | GS | ||||
| 生石灰(乾燥) | 中 | 強アルカリ性 | ○ | △ | △ | DT | ||
| 消石灰(乾燥) | 小 | 強アルカリ性 | ○ | △ | △ | 〃 | ||
| ポリエチレン | 中 | 中性 | ○ | △ | △ | 〃 | ||
| 塩ビ粉末 | 中 | △ | △ | MT | ||||
| カーボン | 中 | 中性 | ○ | △ | △ | BT | ||
| 活性炭 | 中 | 中性 | ○ | △ | △ | DT | ||
| 塩安(乾燥) | 小 | 中性 | ○ | △ | △ | 〃 | ||
| 硫安(乾燥) | 中 | 酸性 | ○ | △ | △ | 〃 | ||
| 尿素粉(乾燥) | 小 | 中性 | ○ | △ | △ | 〃 | ||
| 尿素粉(湿) | 中 | 強アルカリ性 | ○ | △ | △ | GS | ||
| 合成洗剤 | 中 | 中性 | ○ | △ | △ | DT | ||
| 石膏(湿) | 中 | 強酸性 | ○ | ○ | ○ | GS・RT | ||
| ドロマイト | 中 | アルカリ性 | ○ | △ | ○ | △ | DT | エプロンコンベヤの場合 DTA仕様 |
| 石灰石(乾燥) | 中 | アルカリ性 | ○ | △ | ○ | △ | 〃 | エプロンコンベヤの場合 DTA仕様 |
| 粘土(乾燥) | 中 | 中性 | △ | △ | BT | |||
| セメントクリンカー | 大 | 強アルカリ性 | ○ | △ | ○ | △ | CT | |
| セメント製品 | 中 | 強アルカリ性 | ○ | ○ | CT | |||
| ウッドチップ(乾燥) | 小 | アルカリ性 | ○ | △ | DT | |||
| おがくず(乾燥) | 小 | アルカリ性 | ○ | △ | DT | |||
| 石炭 | 中 | 酸性 | ○ | ○ | CT | |||
| コークス | 大 | 中性 | ○ | △ | BT | |||
| アルミナ | 中 | 強アルカリ性 | △ | △ | CT | |||
| 鋳物砂 | 大 | 中性 | ○ | △ | BT | |||
| スケール | 中 | 中性 | ○ | △ | △ | BT | ||
| コークスダスト | 大 | 中性 | △ | BT | ||||
| 石灰ダスト(湿) | 中 | 酸性 | △ | BT | ||||
| クリンカーダスト | 大 | 強アルカリ性 | △ | BT | ||||
| 生ゴミ | 中 | △ | ○ | RT | ||||
| 都市ゴミ焼却灰 (常温・乾燥) |
小 | アルカリ性 | ○ | DTA | ||||
| 都市ゴミ焼却灰 (水分含む) |
小 | アルカリ性 | ○ | RT | ||||

