技術資料 大形コンベヤチェーンスプロケット 取扱
1. 据付
スプロケットの取付けの良否は、コンベヤのスムーズな運行に大きな影響を与え、コンベヤチェーンの寿命を左右します。取付けは下記要領で正しく行ってください。
取付精度は、コンベヤチェーン自体からみた一般的な値です。コンベヤ本体の精度上から制限がある場合には、それに準じてください。
1.1 軸の取付精度
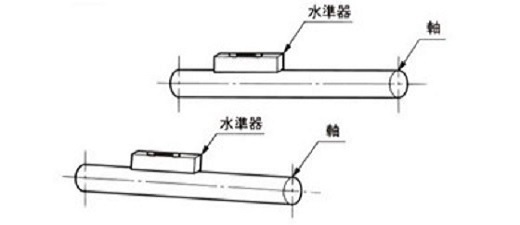
1.1.1 軸の水平度
精度は±1/300の範囲に水準器で調整してください。
図1.軸の水平度の測定
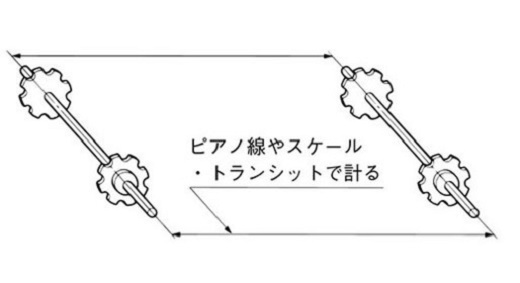
1.1.2 軸の平行度
軸の平行度はスケールなどを用いて±1mmに調整してください。
図2.軸の平行度の測定
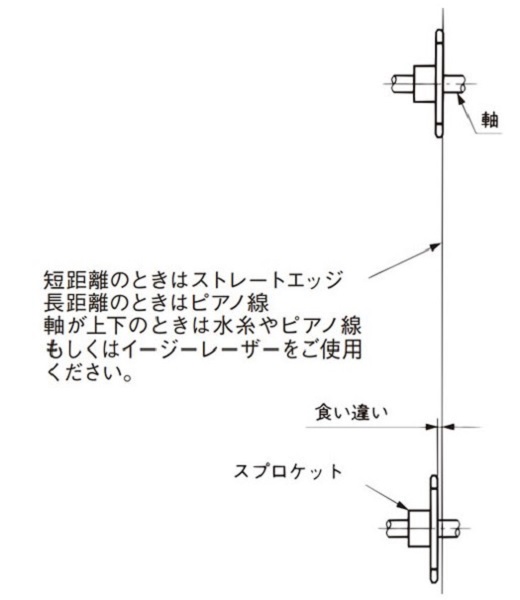
1.1.3 一対のスプロケットの食い違い
- ・軸間距離1mまでのとき:±1mm以下
- ・軸間距離1m~10m未満のとき:±軸間距離(mm)1000以下
- ・軸間距離10m以上のとき:±10mm以下
図3.スプロケットの食い違いの測定
1.1.4 スプロケットの固定
正しい位置が決まったスプロケットは、キーなどで軸に固定します。
並列使用のスプロケットは、軸心上の2組以上のスプロケット歯を同位相にします。
並列使用と指定のうえ、当社でキー加工した場合は、ハブに合マークを刻印しています。
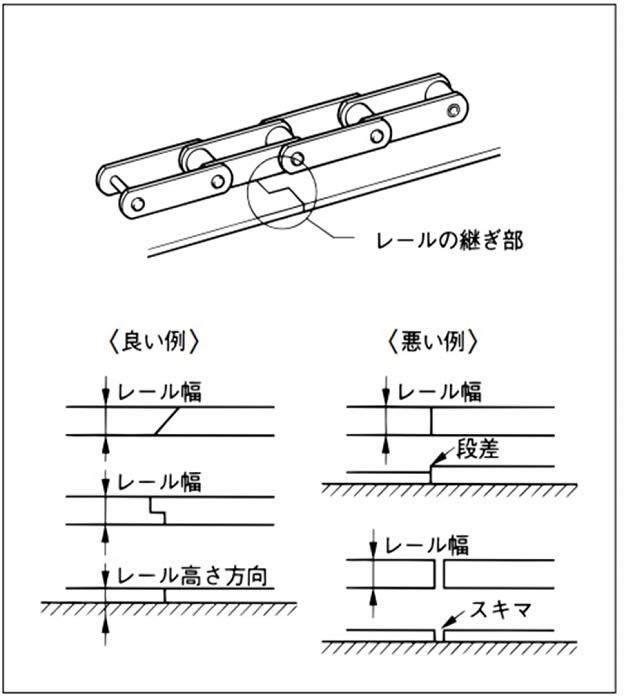
1.2 コンベヤチェーン用レール
- 1)下図のようにレールの継ぎ部は円滑にしてください。エッジは取除く、段差、隙間はなくしてください。)
- 2)溶接時のスパッタやスケールは取除いてください。
- 3)試運転時は無負荷でチェーンに給油し、チェーンとレールの状態を確認してください。
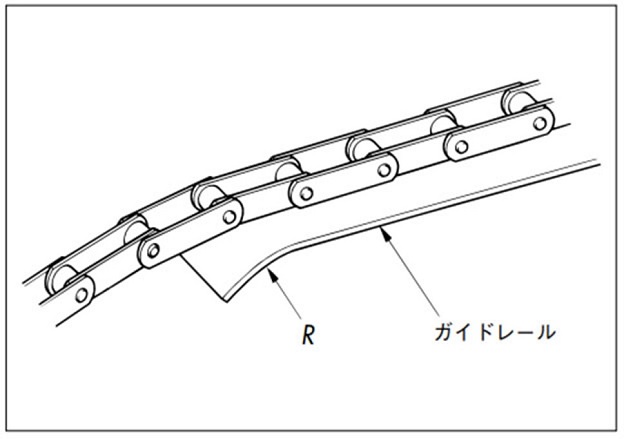
- 4)チェーンの出入口
ガイドレールにRを付けて、チェーンの運行を滑らかにします。
レールの継ぎ部
チェーンの出入口ガイドレール