技術資料 減速機 DCブラシレスモータ 選定
選定手順や注意事項等をご覧になりたい方は下記へお進みください。
製品シリーズの絞り込みや仮選定をご希望の方は
こちらをクリックしてください。
使用条件が決まっており詳細な選定をご希望の方は
こちらをクリックしてください。
選定
運転サイクル・負荷トルク等により、当社にてモータ容量の選定が可能です。
お問い合わせの際は選定依頼用シートをご利用ください。
1. 条件
(1) 運転サイクル
出力軸回転速度
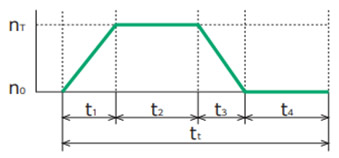
- nT:出力軸最高回転速度(r/min)
- t1:加速時間(sec)
- t2:定常時間(sec)
- t3:減速時間(sec)
- t4:停止時間(sec)
- tt:1サイクルの時間(sec.)
出力トルク
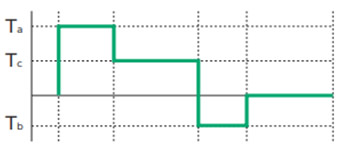
- Ta:加速トルク(N・m)
- Tc:定常トルク(N・m)
- Tb:減速トルク(N・m)
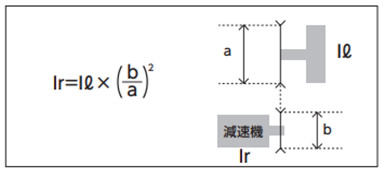
(2) 負荷慣性モーメント Ir
慣性モーメントの求め方の表より減速機の出力軸上の負荷慣性モーメントIrを算出
Ir:減速機出力軸上負荷慣性モーメント(kg・m2)
(3) 加減速トルク Ta, Tb
加速トルク Ta = △Ta + Tc
減速トルク
△Ta = 2πIr × △na 60 × t1
Tb = △Tb - Tc
△Tb = 2πIr × △nb 60 × t3
- Ir:減速機出力軸上負荷慣性モーメント(kg・m2)
{Ir + (Ig + Im) × i2}
(モータ軸換算減速部慣性 + モータ慣性) × 速比^2 (慣性モーメント資料) - △Ta:慣性加速トルク(N・m)
- △na:回転速度差(r/min) △na = nT - no
- △Tb:慣性減速トルク(N・m)
- △nb:回転速度差(r/min) △nb = nT - no
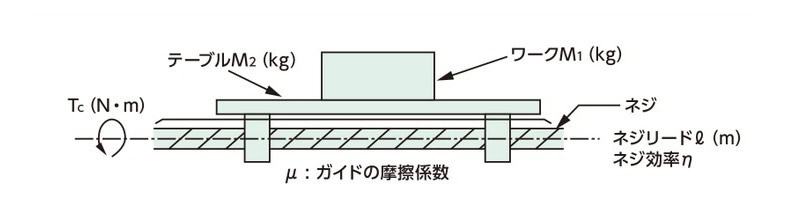
(4) 定常トルク Tc
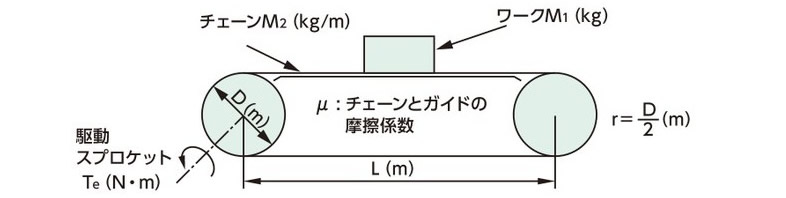 |
Tc = G(M1 + 2.1 × M2 × L) × μ × r G = 重力加速度:9.80665m/s2 |
 |
Tc = G(M1 + M2) × μ × ℓ 2 × π × η |
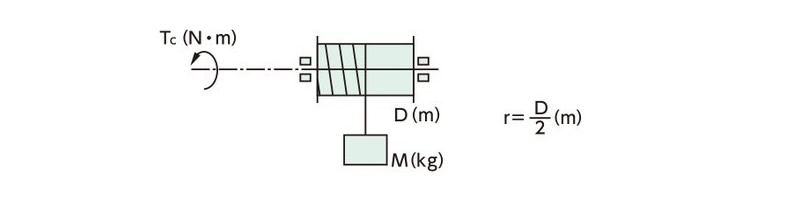 |
Tc = GM × r |
2. 選定手順
| (1) 減速比 i を算出 |
i ≒
Nm
nT
Nm:モータ回転速度 |
||||||||
| ↓ | |||||||||
| (2) 平均出力トルクを算出 |
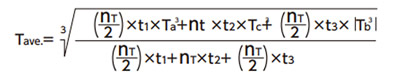
|
||||||||
| ↓ | |||||||||
| (3) サイズの決定
平均トルク 最大トルク |
fs:シリーズ係数
最大トルク < 減速機出力軸最大トルク |
||||||||
| ↓ | |||||||||
| (4) 平均出力軸回転速度nave.を算出 |
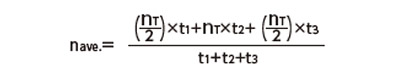
|
||||||||
| ↓ | |||||||||
| (5) 回転速度の確認 nave. × i < 減速機定格入力回転速度 nT × i < 減速機最高入力回転速度 |
|
||||||||
| ↓ | |||||||||
| (6) 出力軸ラジアル荷重の確認 | O.H.L < N:減速機許容ラジアル荷重※ O.H.L = 2000 × Ta × f × Lf D D:スプロケットなどのピッチ円直径(mm) |
||||||||
※伝動能力表の許容ラジアル荷重をご参照ください。
f:O.H.L.係数
| チェーン | ギヤ歯付ベルト | Vベルト |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 1.25 | 1.5 |
Lf:作用位置係数
| ℓ/Q | 0.25 | 0.38 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lf | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
基準長さ:Q
| 形番 | 速比 | Q |
|---|---|---|
| DCHM020 | 10 ~ 60 | 36 |
| DCHM040 | 10 ~ 50 | 42 |
| DCHM075 | 10 ~ 50 | 58 |
シリーズ係数:fs
| 形番 | シリーズ係数 |
|---|---|
| DCHM | 1.7 |
中空出力軸
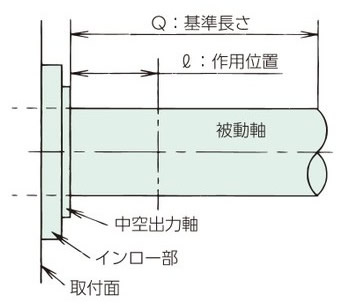
Q:基準長さは左表をご参照ください。
中実出力軸
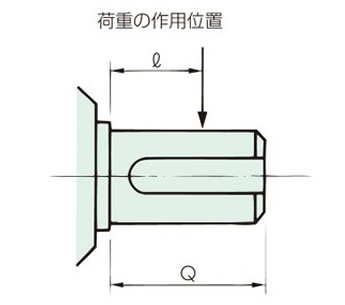
Q:基準長さは各タイプの寸法表をご参照ください。
3. 出力軸オーバーハングロードの確認
出力中央軸にスプロケット、ギヤ、ベルトなどを取り付ける場合、また中空軸にケースタップを使って取り付ける場合には、出力軸に作用するオーバーハングロードが、使用する小形ギヤモータの許容O.H.L.以下になることを確認ください。
※強力歯付ベルト使用時には表1のO.H.L.係数(f)によらず取付張力を加えて計算してください。
[オーバーハングロード計算]
許容O.H.L. ≧ 2000 × TF × f × Lf Dp
- TF:補正トルク
- f:OHL係数(表1)
- Lf:作用位置係数(式1)
- Dp:スプロケットなどのピッチ円直径(mm)
基準長さ:Q
| 形番 | 速比 | Q |
|---|---|---|
| DCHM020 | 10 ~ 60 | 36 |
| DCHM040 | 10 ~ 50 | 42 |
| DCHM075 | 10 ~ 50 | 58 |
表1.O.H.L.係数:f
| チェーン | ギヤ歯付ベルト | Vベルト |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 1.25 | 1.5 |
式1.作用位置係数:Lf
| ℓ/Q | 0.25 | 0.38 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lf | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| 中実軸 | 中空軸 |
|---|---|

Q:基準長さは各タイプの寸法表をご参照ください。 |

Q:基準長さは左表をご参照ください。 |
4. モータ軸換算慣性モーメント
| 形番 | 減速比 |
慣性モーメント ×10-4kg・m2 |
|---|---|---|
| DCHM020-20H | 10 | 0.065 |
| 15 | 0.050 | |
| 20 | 0.045 | |
| 25 | 0.041 | |
| 30 | 0.040 | |
| 40 | 0.039 | |
| 50 | 0.038 | |
| 60 | 0.037 | |
| DCHM040-30H | 10 | 0.117 |
| 15 | 0.076 | |
| 20 | 0.060 | |
| 25 | 0.051 | |
| 30 | 0.047 | |
| 40 | 0.056 | |
| 50 | 0.052 | |
| DCHM075-35H | 10 | 0.306 |
| 15 | 0.209 | |
| 20 | 0.170 | |
| 25 | 0.146 | |
| 30 | 0.140 | |
| 40 | 0.158 | |
| 50 | 0.145 |
| 形番 | 減速比 |
慣性モーメント ×10-4kg・m2 |
|---|---|---|
| DCHM020-22U | 10 | 0.068 |
| 15 | 0.051 | |
| 20 | 0.046 | |
| 25 | 0.041 | |
| 30 | 0.040 | |
| 40 | 0.039 | |
| 50 | 0.038 | |
| 60 | 0.037 | |
| DCHM040-28U | 10 | 0.133 |
| 15 | 0.083 | |
| 20 | 0.065 | |
| 25 | 0.054 | |
| 30 | 0.049 | |
| 40 | 0.059 | |
| 50 | 0.054 | |
| DCHM075-38U | 10 | 0.347 |
| 15 | 0.227 | |
| 20 | 0.180 | |
| 25 | 0.152 | |
| 30 | 0.145 | |
| 40 | 0.165 | |
| 50 | 0.149 |
DCブラシレスモータ
| モータ容量 | ブレーキ |
慣性モーメント ×10-4kg・m2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2kW | ブレーキ無 | 1.154 |
| ブレーキ付 | 1.159 | |
| 0.4kW | ブレーキ無 | 1.753 |
| ブレーキ付 | 1.780 | |
| 0.75kW | ブレーキ無 | 12.761 |
| ブレーキ付 | 12.918 |

