技術資料 トップチェーン 選定
選定手順や注意事項等をご覧になりたい方は下記へお進みください。
製品シリーズの絞り込みや仮選定をご希望の方は
こちらをクリックしてください。
使用条件が決まっており詳細な選定をご希望の方は
こちらをクリックしてください。
プラローラテーブルの選定
下記手順に沿って、搬送条件に最も適したプラローラテーブルとレールの選定を行ってください。
- 1. 搬送条件の確認
- 2. チェーン形式の選定
- 3. チェーンサイズの選定
- 4. 所要動力の計算
手順1. 搬送条件の確認
搬送条件の確認を行ってください。
搬送条件確認項目
| 1.搬送物 | (1)材質 |
|---|---|
| (2)1個当たりの質量 g/個 | |
| (3)寸法(縦×横) mm | |
| 2.搬送経路 | (1)搬送レイアウト |
| (2)コンベヤ長さ m | |
| (3)スペース m | |
| 3.搬送条件 | (1)搬送量 /min |
| (2)搬送間隔 mm | |
| (3)コンベヤ速度 m/min | |
| 4.使用雰囲気 | (1)温度 ℃ |
| (2)薬品、水、湿度などの腐食条件(各種液体に対する耐食性参照)(有の場合、液体名称) |
2-(4)搬送レイアウト・その他メモ
手順2. チェーン形式の選定
ST形...搬送物の横移載(横入れまたは横出し)がある場合に使用します。
RT形...搬送物の横移載がない(直入れ・直出し)場合に使用します。(ただし搬送物がパレットやケースなどの大きな物の場合は横移載も可能です。)
手順3. チェーンサイズの決定
プラローラテーブルのチェーンサイズは、表1.搬送物による選定表と表2.プラローラテーブルST形、RT形の搬送能力表によって選定してください。
注)走行レールについては走行レールの項を参照ください。
表1.搬送物寸法による選定表
| チェーンサイズ | 搬送物寸法 (mm) |
|---|---|
| 300シリーズ | 30以上 |
| 400シリーズ | 44以上 |
| 500シリーズ | 55以上 |
| 600シリーズ | 66以上 |
注)搬送物寸法は搬送物の底寸法を表しています。なお、搬送物寸法は底寸法と高さのバランスによって異なりますので目安としてください。
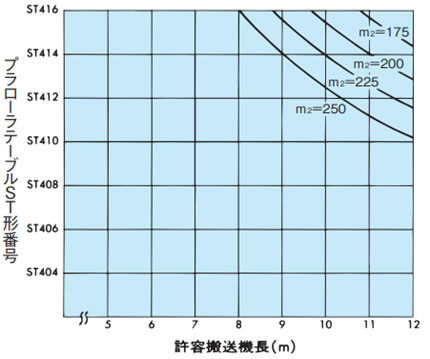
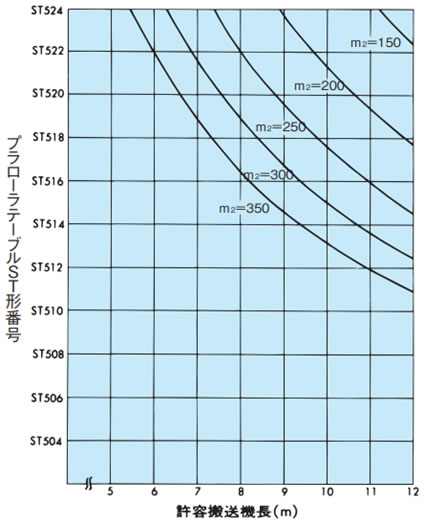
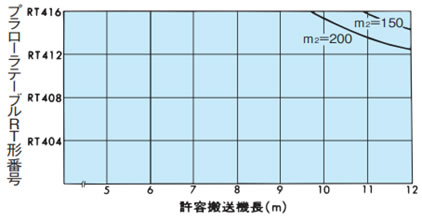
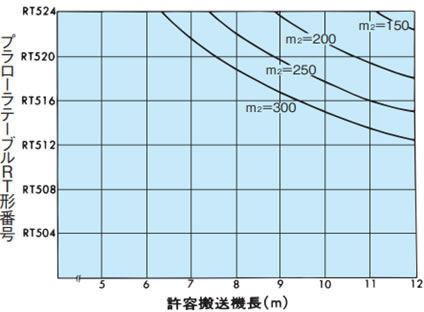
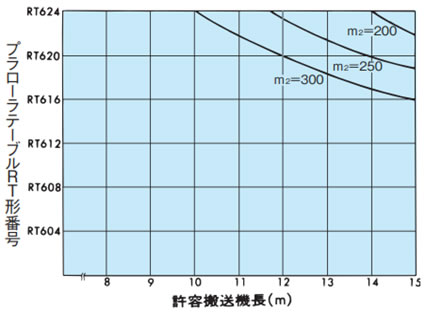
表2. プラローラテーブルST形、RT形の搬送能力表
| 表の見方:ST形 | 表の見方:RT形 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
m2 = 300kg/m2 機長=10mの場合はST504~ST514の m2 = 載荷質量(kg/m2) = 搬送物質量(kg) 搬送物の底面積(m2) ST300
ST400
ST500
|
m2 = 300kg/m2 機長=10mの場合はST504~ST514の m2 = 載荷質量(kg/m2) = 搬送物質量(kg) 搬送物の底面積(m2) RT300
RT400
RT500
RT600
|
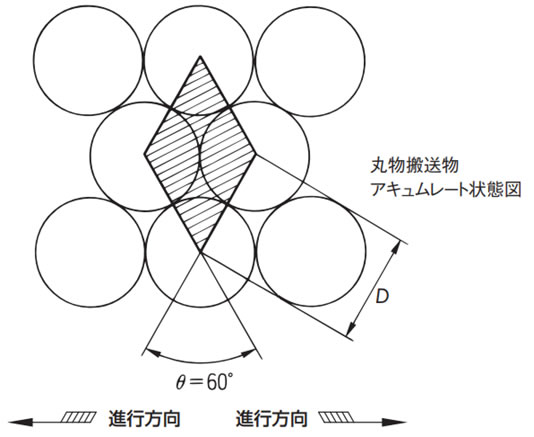
・載荷質量m2(kg/m2)の求め方(丸物の場合)
m2 = 載荷質量(kg/m2) = 搬送物質量(kg) 搬送物の底面積(m2)
m2 = ω × 106 D2sin60° (kg/m2)
- m2:載荷質量(kg/m2)
- ω:搬送物1個の質量(kg)
- D:搬送物の外径(mm)
例)350ml缶(外径Φ66、0.37kg/本の場合)
m2 = 0.37 × 106 662 × sin60° = 98kg/m2
手順4. 所要動力の計算
所要動力は次式によって求めます。
kW = X・(m1 + m2・H)・S・v 5565・η
- kW = 所要動力
- m1 = チェーン概略質量(kg/m)
- m2 = 載荷質量(kg/m2)
- H = 搬送幅[有効幅](m)
- S = 軸間距離(m)
v = チェーンスピード(m/min)
η注) = 駆動部の伝達機械効率
X = 潤滑係数(摩擦係数とは異なります)
- ・チェーン本体部潤滑ありの場合 X = 0.3
- ・チェーン本体部潤滑なしの場合 X = 0.4
注)伝達機械効率は、使用される駆動装置をご確認ください。