技術資料 直動機器 リニパワージャッキ 取扱
用語・説明
1. 基本容量:
ジャッキが保持できる、または昇降できる最大荷重。ただし、負荷の性質によって使用係数(Sf)を含んだ荷重で選定・使用する必要あり。
2. ネジ外径・ネジ谷底径:
下図参照。
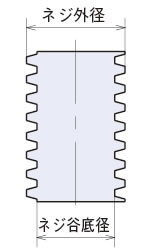
[台形ネジ]
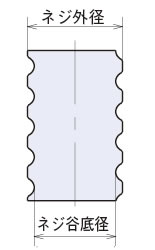
[ボールネジ]
3. ネジリード:
ジャッキにおいてはウォームホイル一回転あたりに対するネジ軸(トラベリングナット仕様の場合はナット)の軸方向移動量。
4. ストローク:
ネジ軸(トラベリングナット仕様の場合はナット)の移動可能な距離。
寸法図のXMAX-XMIN。
5. ウォーム速比:
ウォームホイルを一回転させるのに必要な入力軸の回転数。
(入力軸とウォームホイルの減速比)
6. 総合効率:
ネジ効率とウォーム効率を含んだジャッキ全体の運転効率。
7. 最大許容入力容量:
荷重とネジ軸速度(入力回転速度)の関係を規定する入力容量の許容値。
負荷時間率(%ED)、ジャッキ減速部の表面温度(MAX. 80℃)を超えない範囲で使用のこと。
8. 無負荷空転トルク:
無負荷状態で入力軸の回転に要する入力トルク。
9. 保持トルク:
基本容量と同一荷重を保持する際の入力軸に必要な入力トルク。
10. 許容入力軸トルク:
入力軸のみの許容トルクのことで軸強度より制限を受ける。
ジャッキを直列連動する場合に、自身に必要なトルクと他のジャッキへ伝えるトルクとの和が許容値以下となるよう制限する。
11. 基本容量に対する所要入力トルク:
基本容量と同一荷重を昇降する際の入力軸に必要な入力トルク。
12. 入力軸一回転当りのネジ移動量:
入力軸一回転あたりに進むネジ軸(トラベリングナット仕様の場合はナット)の移動量。
13. 基本容量における最大入力回転速度:
基本容量と同一荷重を昇降する際の入力軸に入力できる最大回転速度。
14. 基本容量時のネジ軸回転トルク:
基本容量と同一荷重を昇降する際にネジ軸(トラベリングナット仕様の場合はナット)が自転しようとする回転トルク。
装置側、ジャッキ側のいずれかで回り止め対策を行わないとネジとナットが共回りして昇降しない。
15. 許容荷重:
ジャッキのネジ軸速度(入力回転速度)が決まり、最大許容入力容量から計算にて算出できる荷重。
16. 座屈:
ジャッキのネジ軸は断面に比べて軸の長さが長いために、ネジ軸方向の圧縮力がある値を超えるとネジ軸が安定を失い、急激に大きな曲げ変形を生じる。このことを座屈という。
座屈荷重は支持方法(据付状態)によって異なる。
17. 許容ネジ軸回転速度:
ネジ軸は自重たわみの下で回転し、回転速度がネジ軸の固有振動数に近づいたとき共振を発生し振動を起こす。よって共振点(危険回転速度)より低い回転速度で使用する必要がある。
共振点を許容ネジ軸回転速度という。ジャッキではネジ軸が回転するトラベリングナット仕様で検討が必要。
18. 惰行距離:
リミットスイッチ、または停止ボタンが作動して停止するまでの距離。
この惰行距離は、荷重条件やブレーキ特性、操作回路によって変化する。
19. 停止精度:
起動・停止を繰り返したときの停止位置のバラツキ量。
20. セルフロック:
ブレーキ装置がないジャッキ単体の状態で荷重を保持できることをいう。
JWM(台形ネジタイプ)の全枠番002~1000は計算上でセルフロックが働く。
21. 負荷時間率:
負荷時間率(%EDともいう)とは1サイクルに占める運転時間の割合。
負荷時間率(%ED) = 1サイクルの運転時間 1サイクルの運転時間 + 休止時間 ×100(%)
22. 発生推力:
モータ付、ギヤモートル付ジャッキ単体においてモータ定格トルクより換算した推力(最大の昇降荷重)。
ただし、他のジャッキと駆動部付ジャッキを連動運転する場合は選定が必要。
23. ボールネジ寿命:
ボールネジの寿命はボール転動面の疲労による剥離(Flaking)によって決まり、剥離が生じるまでのネジ軸(ナット)の総走行距離で表す。
この疲労による剥離現象は同じものを多数同条件下で運転してもある範囲でばらつきが生じる。
全体の90%以上が剥離を起こさずに達し得る寿命を定格寿命(B10寿命)という。

