技術資料 パワーロック 選定と手順
選定手順や注意事項等をご覧になりたい方は下記へお進みください。
製品シリーズの絞り込みや仮選定をご希望の方は
こちらをクリックしてください。
使用条件が決まっており詳細な選定をご希望の方は
こちらをクリックしてください。
AEシリーズの選定
1. 最大発生トルクと最大発生スラスト荷重の確認
発生する伝達容量に使用係数を見込んで、最大発生トルクと最大発生スラスト荷重を求めます。
※サーボモータ・ステッピングモータの締結の場合は、それぞれの最大トルク(ピークトルク)を最大発生トルク(Tmax)としてください
| SI単位 |
|---|
|
Tmax = 9550 × H n ・f Tmax = 最大発生トルク(N・m)
|
| 重力単位 |
|---|
|
Tmax = 974 × H n ・f Tmax = 最大発生トルク(kgf・m)
|
Pmax = Pax・f
- Pmax:最大発生スラスト荷重 kN{kgf}
- Pax:スラスト荷重 kN{kgf}
- f:使用係数
f:使用係数
| 負荷の状態 | 使用係数 | |
|---|---|---|
| 衝撃のない円滑な負荷 | 慣性小 | 1.5~2.5 |
| 軽い衝撃のある負荷 | 慣性中 | 2.0~4.0 |
| 大きな衝撃のある負荷 | 慣性大 | 3.0~5.0 |
トルクのみかかる場合
以上より求められた、Tmaxとカタログ伝達トルクMtを比較します。
Mt ≧ Tmax → 使用できます。
Mt < Tmax → 形番アップを検討ください。
トルクとスラスト荷重が同時に加わる場合
合成負荷MRを算出し、伝達トルクMtと比較します。
MR = Tmax2 + (Pmax × d 2 )2
- Tmax:最大発生トルク N・m{kgf・m}
- Pmax:最大発生スラスト荷重 N{kgf}
- d:軸径 m
以上より求められた、MRとカタログ伝達トルクMtを比較します。
Mt ≧ MR → 使用できます。
Mt < MR → 形番アップを検討ください。
*本シリーズは複数個での使用はできません。
2. 軸とボスの検討
(1) 材料強度の検討
軸およびボスには締結時に大きな面圧が作用します。軸およびボスは次式を満足する強度がある材質のものをご使用ください。
σ0.2S ≧ 1.2 × P σ0.2B ≧ 1.2 × P'
- P :軸側面圧 MPa{kgf/mm2}
- P':ボス側面圧 MPa{kgf/mm2}
- σ 0.2S:使用軸材料の降伏点応力 MPa{kgf/mm2}
- σ 0.2B:使用ボス材料の降伏点応力 MPa{kgf/mm2}
鉄鋼材料の強度一覧表には、代表的な鉄鋼材料の降伏点の値を示していますので、参照ください。
(2) ボス外径の検討
AEシリーズの主要諸元ページを参照ください。
一覧表に記載がない材質については、次式に従い必要ボス外径を算出してください。
ボス外径 DN ≧ D σ0.2B + K3・P' σ0.2B - K3・P'
- DN:ボス外径 mm
- D :ボス内径 mm
- P':ボス側面圧 MPa{kgf/mm2}
- σ 0.2B:使用ボス材料の降伏点応力 MPa{kgf/mm2}
- K3:ボス形状係数(各製品の主要諸元ページを参照ください。)
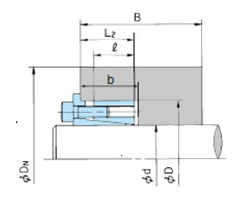
(3) 中空軸内径の検討
中空軸内径は次式にて算出してください。
中空軸内径 dB ≦ d × σ0.2S - 2・P・K3 σ0.2S
- dB:中空軸内径 mm
- d:軸径 mm
- P:軸側面圧 MPa{kgf/mm2}
- σ0.2S:使用軸材料の降伏点応力 MPa{kgf/mm2}
- K3:ボス形状係数(各製品の主要諸元ページを参照ください。)
3. ラジアル荷重
ベルト駆動などのように、ラジアル荷重がパワーロックに作用する場合、次式でラジアル荷重によって発生する軸側、ボス側の面圧 Prad、P'radを算出し、軸側、ボス側面圧とカタログ面圧を比較して、表3の許容値以内であることを確認してください。
Prad = 1.3 × Pr d × ℓ
P'rad = 1.3 × Pr D × ℓ
- Pr:ラジアル荷重 N{kgf}
- ℓ:ボスとアウタリングの接触面幅 mm
- d:軸径 mm
- D:ボス内径 mm
- P:軸側面圧 MPa{kgf/mm2}
- P':ボス側面圧 MPa{kgf/mm2}
このようなラジアル荷重が作用するときの必要ボス外径Dnや中空軸内径dBを求める場合は、それぞれP、P'にPrad、P'radを加算して計算ください。
| シリーズ | Prad(P'rad)/P(P') |
|---|---|
| AE | 20%以下 |

